Study the diagrams below and in the spaces below, state (1) the place(s) of articulation, (2) the manner of articulation of each sound. In addition, give (3) the IPA symbols and (4) descriptions of the possible phone(s) that is depicted in each illustration and (5) an example of an English word beginning with the sound(s) illustrated in each.
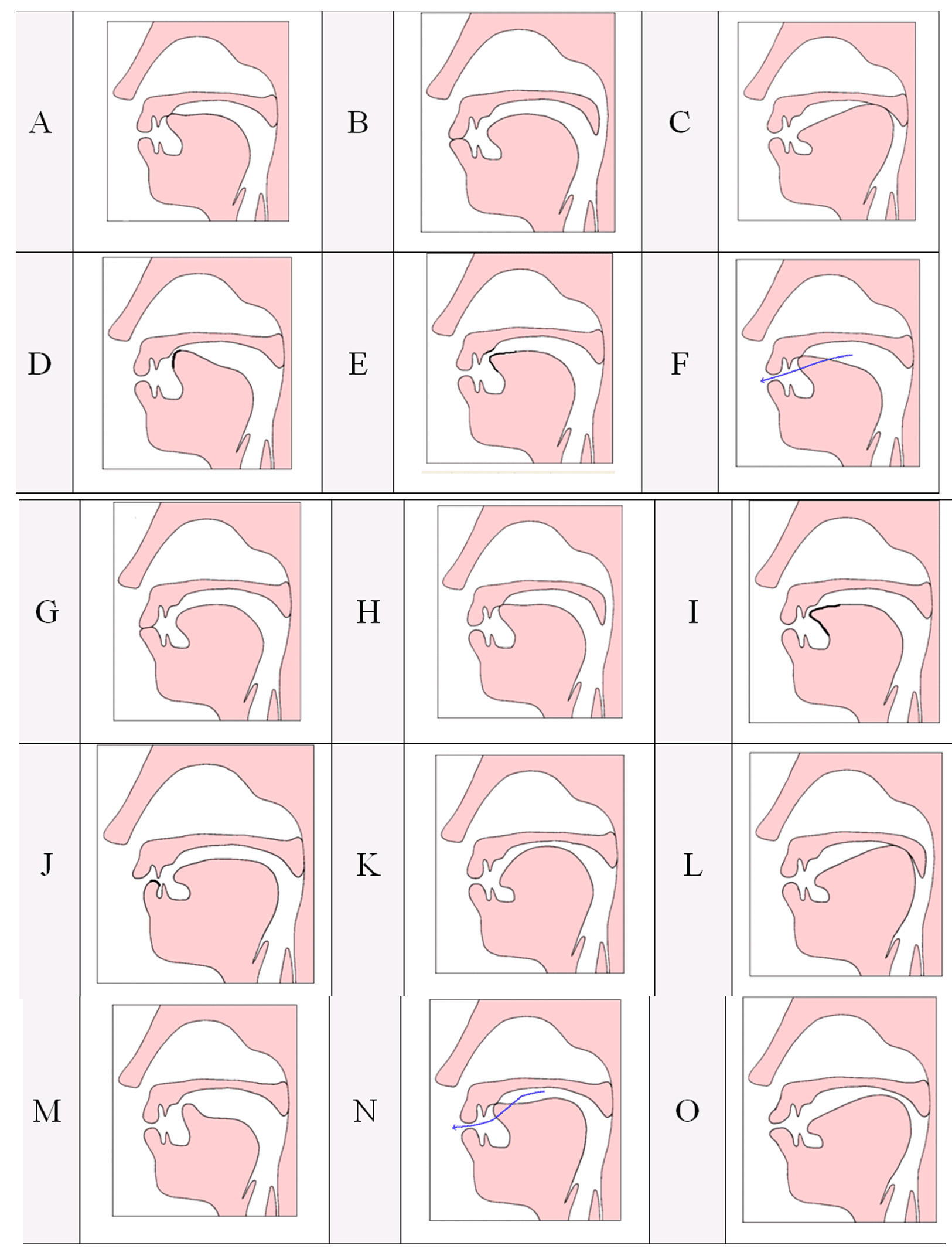
Diagram: A
Place of Articulation: Tip or blade of the tongue & alveolar ridge
Manner of Articulation: Plosive
IPA Symbol(s): [t] [d]
Description: Alveolar plosive
Example: tap, dad
Diagram: B
Place of Articulation: Labials / lips
Manner of Articulation: Nasal stop
IPA Symbol(s): [m]
Description: Bilabial nasal stop
Example: man
Diagram: C
Place of Articulation: Back of the tongue & velum
Manner of Articulation: Plosive
IPA Symbol(s): [k] [g]
Description: Velar plosive
Example: kit, gum
Diagram: D
Place of Articulation: Blade of the tongue & palato-alveolar region
Manner of Articulation: Fricative
IPA Symbol(s): ![]()
![]()
Description: Palato-alveolar fricative
Example: ship, genre
Diagram: E
Place of Articulation: Tip or blade of the tongue & alveolar ridge
Manner of Articulation: Fricative
IPA Symbol(s): [s] [z]
Description: Alveolar fricative
Example: sun, zip
Diagram: F
Place of Articulation: Centre of blade of the tongue & alveolar ridge
Manner of Articulation: Lateral approximant
IPA Symbol(s): ![]()
Description: Alveolar lateral approximant
Example: late
Diagram: G
Place of Articulation: Labials / lips
Manner of Articulation: Plosive
IPA Symbol(s): [p] [b]
Description: Bilabial plosive
Example: pin, bin
Diagram: H
Place of Articulation: Tip of the tongue & the alveolar ridge
Manner of Articulation: Nasal stop
IPA Symbol(s): [n]
Description: alveolar nasal stop
Example: not
Diagram: I
Place of Articulation: Tip of the tongue & upper teeth
Manner of Articulation: Fricative
IPA Symbol(s): ![]()
![]()
Description: Dental fricative
Example: theatre, this
Diagram: J
Place of Articulation: Lower lip & upper teeth
Manner of Articulation: Fricative
IPA Symbol(s): [f] [v]
Description: Labio-dental fricative
Example: fit, vet
Diagram: K
Place of Articulation: Front of the tongue & hard palate
Manner of Articulation: approximant
IPA Symbol(s): [j]
Description: Palatal approximant
Example: yet
Diagram: L
Place of Articulation: Back of the tongue & velum
Manner of Articulation: Nasal stop
IPA Symbol(s): ![]()
Description: Velar nasal stop
Example: sing
Diagram: M
Place of Articulation: Blade of the tongue & alveolar ridge
Manner of Articulation: Approximant
IPA Symbol(s): ![]()
Description: Alveolar approximant
Example: rat
Diagram: N
Place of Articulation: Centre or blade of the tongue, alveolar ridge & velum
Manner of Articulation: velarized lateral approximant
IPA Symbol(s): ![]()
Description: Velarized lateral approximant or Dark l
Example: bottle
Diagram: O
Place of Articulation: Labials / lips, back of the tongue & velum
Manner of Articulation: approximant
IPA Symbol(s): [w]
Description: Labio-velar approximant
Example: one
2. Describe the position and action of the articulators during the production of the given phones:
The tip of the tongue is brought into a constriction of close approximation with the upper teeth, vocal cords are vibrating
b. [p]
A constriction of complete closure is made at the lips, vocal cords are not vibrating
c. [g]
The back of the tongue forms a constriction of complete closure with the velum, vocal cords are vibrating
d. [t]
The blade of the tongue forms a constriction of complete closure with the alveolar ridge, vocal cords are not vibrating
e. [h]
The vocal cords are brought into a constriction of close approximation, vocal cords are not vibrating
f. ![]()
The blade of the tongue is brought into a constriction of close approximation with the palato-alveolar region, vocal cords are not vibrating
g. [k]
The back of the tongue forms a constriction of complete closure with the velum, vocal cords are not vibrating
h. ![]()
The tip of the tongue is brought into a constriction of close approximation with the upper teeth, vocal cords are not vibrating
i. [s]
The tip or blade of the tongue is brought into a constriction of close approximation with the alveolar ridge, vocal cords are not vibrating
j. [b]
A constriction of complete closure is made at the lips, vocal cords are vibrating
k. [v]
Lower lip is brought close to the upper teeth in a constriction of close approximation, vocal cords are vibrating
l. [z]
The tip or blade of the tongue is brought into a constriction of close approximation with the alveolar ridge, vocal cords are vibrating
This diagram is quite clear and easier to view if it’s saved. The explanations are condense but understandable. Thank you very much. It’s good for practice and revision.
Thank you 🙂 … Glad it is useful.
You are the life saver! Many, many thanks!!
🙂 Happy to be of help, Kaya.
Thank you so much!!!
I’ve been looking all over for pictures to help teach my students proper pronunciation and finally came across this.
Many thanks 🙂
Good afternoon:
I am wondering if I can get the rest of the alphabet with the diagrams with the places of articulation with the description below. I feel it would help me immensely in my ESL classes that I teach online. Some of my individual students could use the extra assistance, as I take the extra steps to help these students learn with less stress and frustration so as to not make them want to give up and quit!
Your assistance would be so very much appreciated.
Thank you ever so kindly,
Angela Williams
These diagrams show the articulation of the consonant phonemes of English, not based on the alphabet. I think I included all the sounds in this one, but it was a long time ago, so will check and get back to you.
thank you! this really helped my understanding
OMG….. !
Nice explanation,
thank you very much, you have been helped may study about phonetics
thank you very much for your aid of making me to understand the consonant phonemes plus there place and manner of articulation. Stay blessed.
this is very helping me 🙂
Thank you so much, i really need this for my presentation next week.